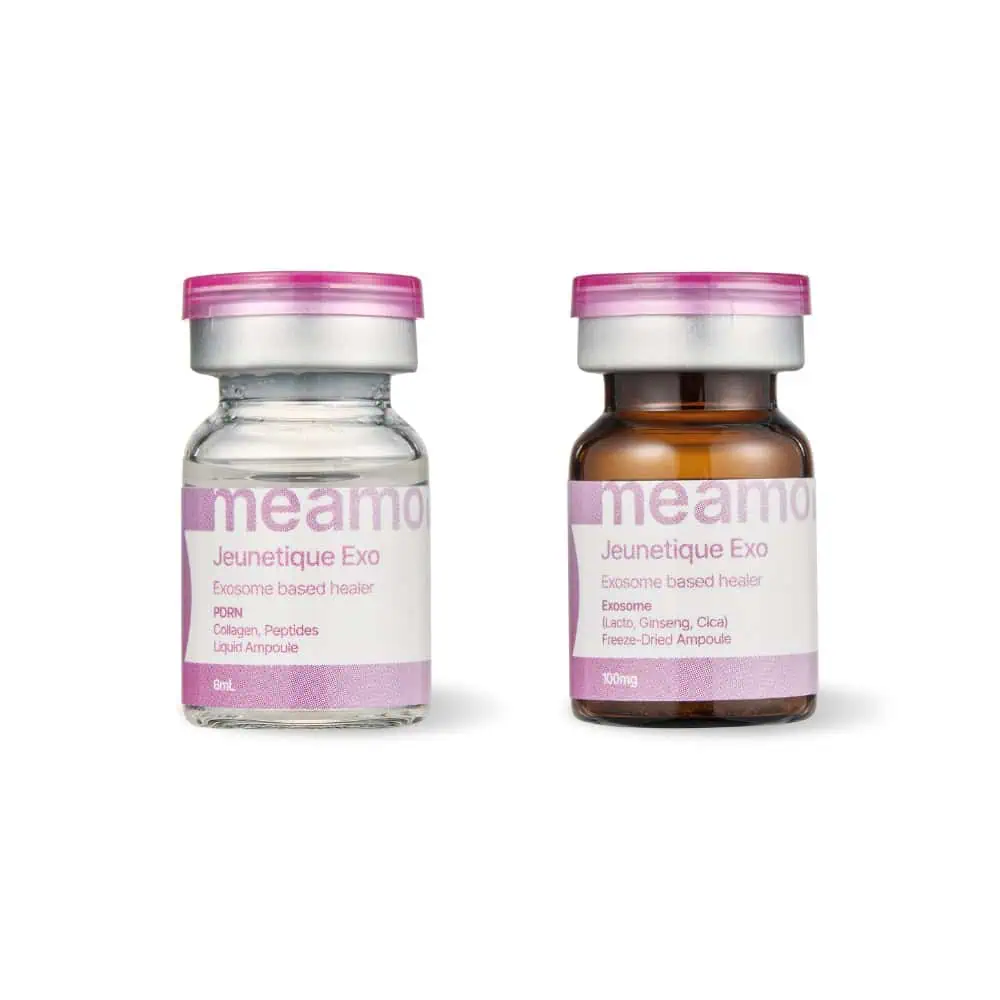
Blogs
Exosomes: A Revolution in Cosmetology and Anti-Aging Therapy
Exosomes are the new buzzword in beauty science. In the last few years, every major cosmetic company has seen it as their duty to launch an anti-ageing product with exosomes. However, in the vast majority of the information materials of these companies, exosomes act as a kind of “philosopher’s stone”.
Here we have added some magic “exosomes” to our product and now they will magically cure all diseases, grant eternal life and turn lead into gold 🙂
But what exactly exosomes are, where they come from, what they contain and, most importantly, why they work so effectively is a mystery shrouded in darkness.
In this article we will tell you from a scientific point of view, with facts and evidence, what exosomes are and how exactly they help to preserve your beauty and youth.
Meamo Labs has decided to go a different way. All our products have a scientific basis and their efficacy has been confirmed by clinical studies and trials. Our new MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosome dermal filler with exosomes is no exception.
At the same time, we realize that only specialists read serious scientific publications and there is almost no information about exosomes for the general public. Therefore, our scientific team decided to create the most comprehensive material on the use of exosomes in cosmetics. This is probably the first article on this complex and very interesting topic, intended for those who are not specialists in medicine and molecular biology (except for one section).
What are exosomes?
They are the tiny nanoscale vesicles that many cells release into the extracellular space. These vesicles were first discovered in sheep in 1983. Since then, many types of extracellular vesicles have been discovered. They turned out to have different origins and different functions. But the easiest way to categorize them was to divide them into three main groups:
-
- exosomes proper, which are between 30 and 200 nm in size,
- microvesicles (200-1000 nm),
- and apoptotic bodies (>1000 nm).
Of these three groups, only the smallest vesicles – exosomes – have been seriously used in cosmetology.
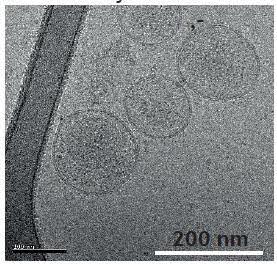
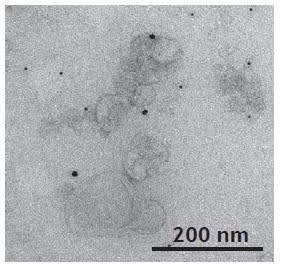
Further studies have shown that virtually all cell types secrete exosomes. In humans, they have been found in plasma and serum, urine, semen, saliva, bronchial fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, breast milk, amniotic fluid, synovial fluid, tears, lymph, bile, and even stomach acid.
In addition, it has become clear that exosomes are produced by all living organisms on our planet, from bacteria to plants and mammals.
Why do we need exosomes?
Initially, scientists thought of exosomes as a kind of “garbage bag”. It was thought that the cell simply puts all sorts of residues from biochemical reactions into this vesicle. And when the exosome fills up, the cell throws it out, beyond its membrane, and gets rid of unnecessary material.
But then it became clear that exosomes are the most important tool of intercellular communication. It’s a universal mechanism that coordinates the work of cells, allowing them to act as a single tissue in the interests of the whole organism. For example, exosomes have been found to be able to:
- Stimulate immune activity, accelerating the immune response to infection.
- Improve nervous system function by promoting myelin formation, neuronal survival and the formation of connections between neurons.
- Accelerate tissue repair and regeneration by increasing cell proliferation and maturation. Slow down aging through paracrine effects.
- Influence reproductive function by participating in germ cell maturation, fertilization and embryo implantation.
- Influence the success of pregnancy by playing a role in maternal-fetal immunologic communication, etc.
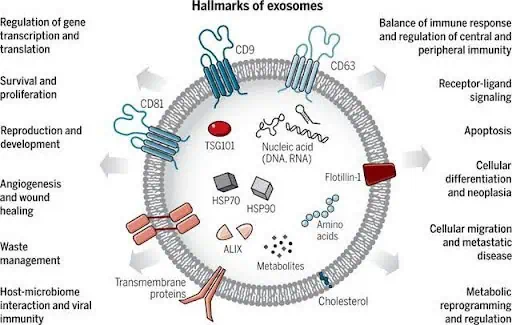
What do exosomes contain?
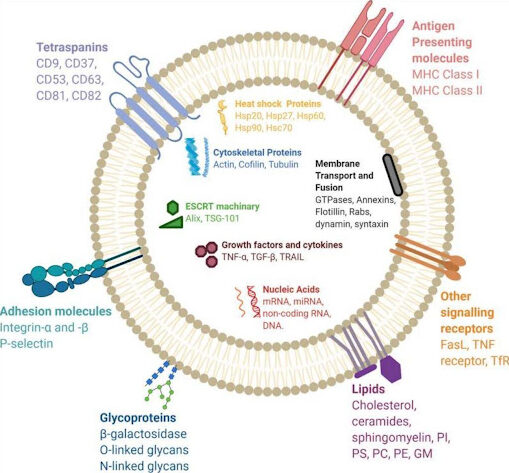
An exosome is a vesicle with a wall made of the same bilayer of phospholipids that make up normal cell membranes. This is why exosomes can easily penetrate target cells – their membrane simply fuses with the cell membrane. The exosome membrane is permeated with a large number of large signaling and adhesive molecules, mostly of a protein nature.
And inside the vesicle is a cargo of dozens of different bioactive components:
- Proteins – cytokines, ribosomal proteins, growth factors, metabolic enzymes.
- Lipids – cholesterol, ceramides and other lipid fractions.
- Nucleic acids – DNA, mRNA and microRNA (miRNA), etc.
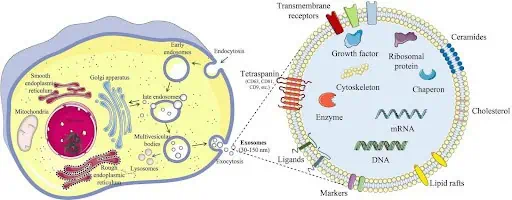
How are exosomes formed?
The biogenesis of exosomes begins with the folding of a portion of the cell membrane inside the cell. This leads to the formation of a large endosome (intracellular vesicle). The endosome is then saturated with bioactive content derived from the cytoplasm of the cell and its Golgi apparatus. Next, even smaller vesicles with a diameter of 30-200 nm - future exosomes - are formed inside the endosome from its membrane. The endosome then fuses with the cell membrane, releasing the exosomes to the outside.
At this stage, it is possible to isolate exosomes from the extracellular environment, purify them and place them in a high-tech cosmetic product. This makes it possible to deliver them as part of this product to the desired area of the skin. And there, as they should, the exosomes will independently move to the target cells (e.g. fibroblasts) and deliver to them the whole “cocktail” of biochemical stimulants.
Why have exosomes become popular in cosmetology and anti-aging therapy?
Exosomes have the unique ability to modulate cellular functions. At the same time, they are one of the few universal “biochemical regulators” that we can control to some extent.
Two properties of exosomes are most commonly used today in cosmetology and anti-aging therapies:
- The ability to accelerate skin recovery from a wide range of damage.
- The ability to inhibit the manifestations of skin aging (e.g. wrinkle formation, moisture loss, etc.).
Advances in molecular biology and medicine have led to an explosion of exosome research. Today, scientific databases contain nearly 20,000 articles on this topic, more than 85% of which were published within the last few years. Many of these papers focus on the use of exosomes in beauty science. We have listed some of them in the table below:
Exosomes for treatment and skin repair
- Qian L., Pi L., Fang B.R., Meng X.X. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate skin wound healing via the lncRNA H19/miR-19b/SOX9 axis. Lab. Invest. 2021;101(9):1254–1266.
- Cao G., Chen B., Zhang X., Chen H. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-19b promotes the healing of skin wounds through modulation of the CCL1/TGF-β signaling Axis. Clin. Cosmet. Invest. Dermatol. 2020;13:957–971.
- Shen K., Wang X.J., Liu K.T., Li S.H., Li J., Zhang J.X., Wang H.T., Hu D.H. [Effects of exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on inflammatory response of mouse RAW264.7 cells and wound healing of full-thickness skin defects in mice] Zhonghua Shaoshang Zazhi. 2022;38(3):215–226.
- Wgealla M.M.A.M., Liang H., Chen R., Xie Y., Li F., Qin M., Zhang X. Amniotic fluid derived stem cells promote skin regeneration and alleviate scar formation through exosomal miRNA-146a-5p via targeting CXCR4. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022;21(10):5026–5036.
- Xiu C., Zheng H., Jiang M., Li J., Zhou Y., Mu L., Liu W. MSCs-derived miR-150-5p-expressing exosomes promote skin wound healing by activating PI3K/AKT pathway through PTEN. Int J Stem Cells. 2022;15(4):359–371.
- Zha J., Pan Y., Liu X., Zhu H., Liu Y., Zeng W. Exosomes from hypoxia-pretreated adipose-derived stem cells attenuate ultraviolet light-induced skin injury via delivery of circ-Ash1l. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2022;39(2):107–115.
- Duan M., Zhang Y., Zhang H., Meng Y., Qian M., Zhang G. Epidermal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin regeneration by downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 in wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020;11(1):452.
- Bakhtyar N., Jeschke M.G., Herer E., Sheikholeslam M., Amini-Nik S. Exosomes from acellular Wharton’s jelly of the human umbilical cord promotes skin wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018;9(1):193.
Exosomes as an anti-aging tool
- Liang J.X., Liao X., Li S.H., Jiang X., Li Z.H., Wu Y.D., Xiao L.L., Xie G.H., Song J.X., Liu H.W. Antiaging properties of exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in photoaged rat skin. BioMed Res. Int. 2020;2020
- Rosmarwati E., Ellistasari E.Y., Kusumawardani A., Julianto I., Widhiati S., Setyawan N.A., Yanuar F. Human platelet lysate-derived exosomes are superior to the lysate at increasing collagen deposition in a rat model of intrinsic aging. J. Appl. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2023:211–216.
- Ge X., Lu L., Bai W., Wang M., Han C., Du H., Wang N., Gao M., Li D., Dong F. The novel roles of bovine milk-derived exosomes on skin anti-aging. bioRxiv. 2023 doi: 10.1111/jocd.16112. 2023.03. 23.532505.
- Han G., Kim H., Kim D.E., Ahn Y., Kim J., Jang Y.J., Kim K., Yang Y., Kim S.H. The potential of bovine colostrum-derived exosomes to repair aged and damaged skin cells. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(2)
- Lee Y., Jeong D.-Y., Jeun Y.C., Choe H., Yang S. Preventive and ameliorative effects of potato exosomes on UVB-induced photodamage in keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2023;28(3):1–10.
- Jo C.S., Myung C.H., Yoon Y.C., Ahn B.H., Min J.W., Seo W.S., Lee D.H., Kang H.C., Heo Y.H., Choi H., Hong I.K., Hwang J.S. The effect of. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022;44(2):526–540.
- Trentini M., Zanolla I., Zanotti F., Tiengo E., Licastro D., Dal Monego S., Lovatti L., Zavan B. Apple derived exosomes improve collagen type I production and decrease MMPs during aging of the skin through downregulation of the NF-κB pathway as mode of action. Cells. 2022;11(24)
- Yan T., Huang L., Yan Y., Zhong Y., Xie H., Wang X. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome miR-29b-3p alleviates UV irradiation-induced photoaging in skin fibroblast. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2022;39(3):235–245.
- Hu S., Li Z., Cores J., Huang K., Su T., Dinh P.U., Cheng K. Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano. 2019;13(10):11273–11282.
- Oh M., Lee J., Kim Y.J., Rhee W.J., Park J.H. Exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells ameliorate the aging of skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19(6)
How do exosomes interact with skin cells?
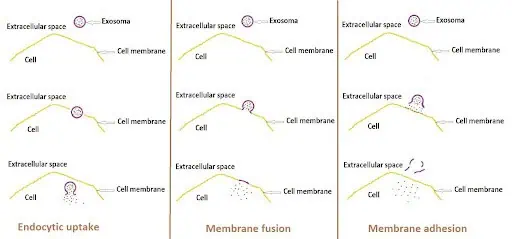
The main advantages of exosomes are their exceptional stability, high biocompatibility, and minimal immunogenicity. This allows them to function as highly efficient targeting transport. Exosomes can deliver their contents to recipient cells in three ways:
- They can enter cells by endocytic uptake.
- They can fuse directly with the cell membrane.
- They can release their “cargo” onto the cell surface, which then takes up these molecules.
Below we will briefly discuss the basic mechanisms of action and the pathways by which exosomes exert beneficial effects on the skin. This is a complex section with a lot of scientific data. You have been warned ☺
✦ Regeneration of damaged skin
Three important exosomal mechanisms that promote skin healing:
- Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway by exosomal miRNA-150-5p
- Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by lipid fractions of exosomes;
- Activation of the TFG-β pathway by exosomal miRNA-19b
Exosomes reduce the intensity of inflammation by suppressing cytokine activity through the NF-κB pathway. In addition, they reduce polysaccharide-induced inflammatory factor mRNA expression.
Exosomes also significantly increased the migration of fibroblasts to the area of skin disease and stimulated their proliferation. An increase in the fibroblast population is a critical component in the healing of any skin lesion.
Finally, recent studies have identified several other specialized signaling pathways associated with skin regeneration: mitogen-activated protein kinase, Notch, TGF-β/Smad, STAT and Hedgehog, CaMKII and Efna3. The main mediators of these pathways are exosomal mRNAs and a variety of proteins.
✦ Slowing skin aging
Skin aging is closely linked to chronic inflammation of the dermis and destruction of structural proteins of the extracellular matrix. The main factor is UV exposure.
Exosomes containing circ-Asch 1l and GPX4 protein fractions have been shown to reverse these effects. They also protect skin cells from UVB-induced damage by limiting the synthesis of the inflammatory cytokines IL6 and TNF-α. Finally, exosomes can target melanocytes and reverse age-related hyperpigmentation.
NB!
Studies have shown that skin cells that were already inflamed responded much more strongly to the exosomes than non-inflamed cells. This means that aging, damaged skin will experience a stronger effect from the MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes.
This is also confirmed by the results of another study, which found that the results of exosome application were much more noticeable in older women than in younger women.
✦ Stimulation of collagen production by fibroblasts
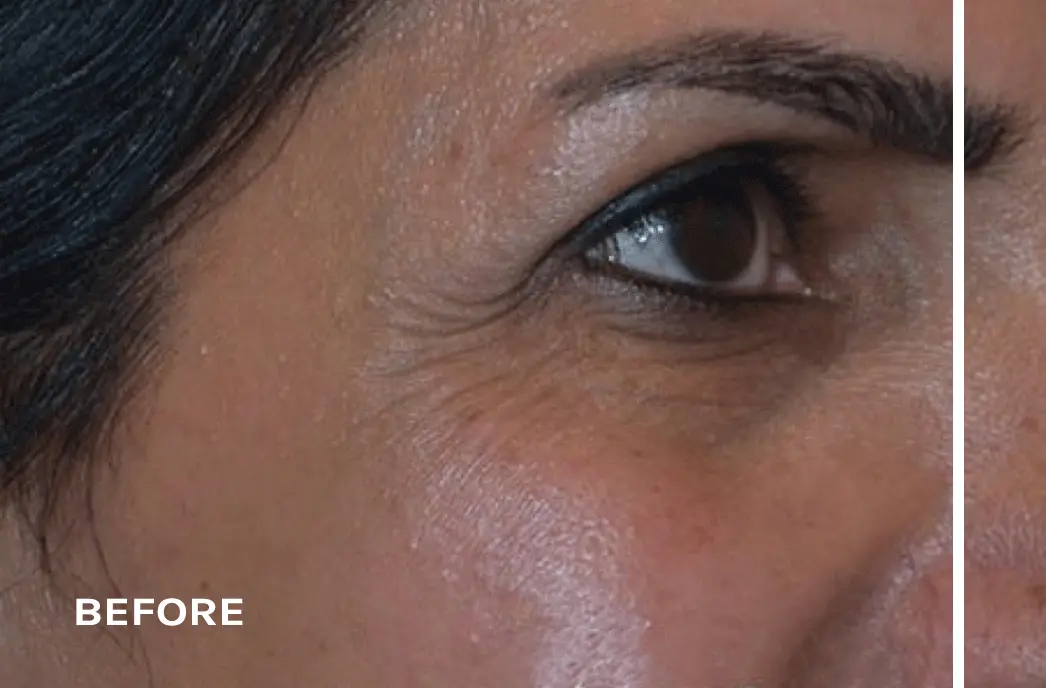

Aging creates a microenvironment with increased levels of oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to the deterioration of dermal fibroblasts. In addition, the production of collagenases, enzymes that degrade intercellular collagen and are encoded by the MMP (metalloproteinase) family of genes, increases.
Several studies show that exosomes can improve the function of aging fibroblasts, restore the expression of collagen types I and III, and suppress the synthesis of MMP1, 2 and 9 enzymes. The formation of a new collagen framework leads to the gradual elimination of fine and medium wrinkles.
✦ Improvement of skin hydration
It has been observed that exosomes directly penetrate keratinocytes and fibroblasts and increase the concentration of natural factors associated with skin hydration. Specifically, the levels of filaggrin (FLG), aquaporin 3 (AQP3) and CD44 increase in keratinocytes and hyaluronidase (HAS2) in fibroblasts.
HAS2 is the enzyme responsible for hyaluronic acid synthesis in fibroblasts, and CD44 is the receptor that binds hyaluronic acid on the outer membrane of keratinocytes. Increasing the concentration of these substances leads to the natural active accumulation and retention of hyaluronic acid in the skin.
Sources of exosomes and their characteristics
Exosomes have been isolated from almost all living organisms on our planet. And scientists have been able to prove that they all help repair the skin and slow down its aging. That is why exosomes are called “universal biochemical language” – it is understood by the cells of all living beings.
Today, the main sources of exosomes for the cosmetic industry are bacteria, plants and human tissues grown under laboratory conditions.
✦ Bacterial exosomes
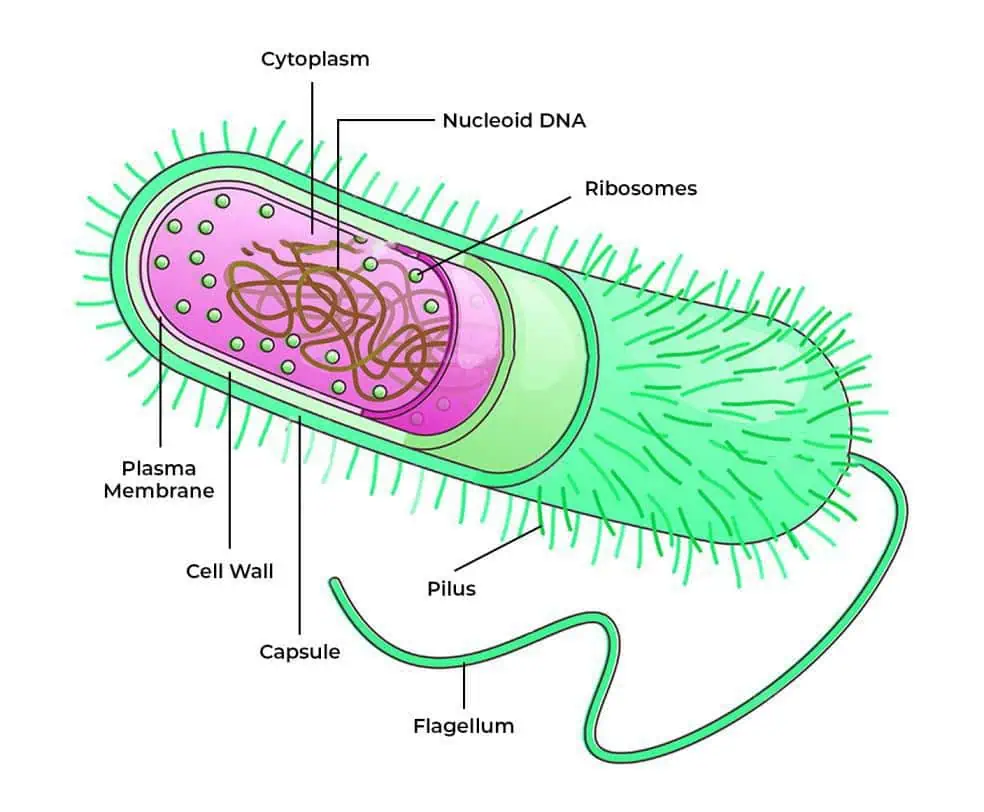
Probiotic bacteria are the most common source. Lactobacilli, for example, are one of the most important components of the normal human microflora. They normally live on our skin and mucous membranes.
There are studies that conclusively prove that exosomes isolated from lactobacilli inhibit the formation of wrinkles and age spots through genetic modulation via mRNA. This is why Lactobacillus exosomes are one of the two exosomal fractions in MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes.
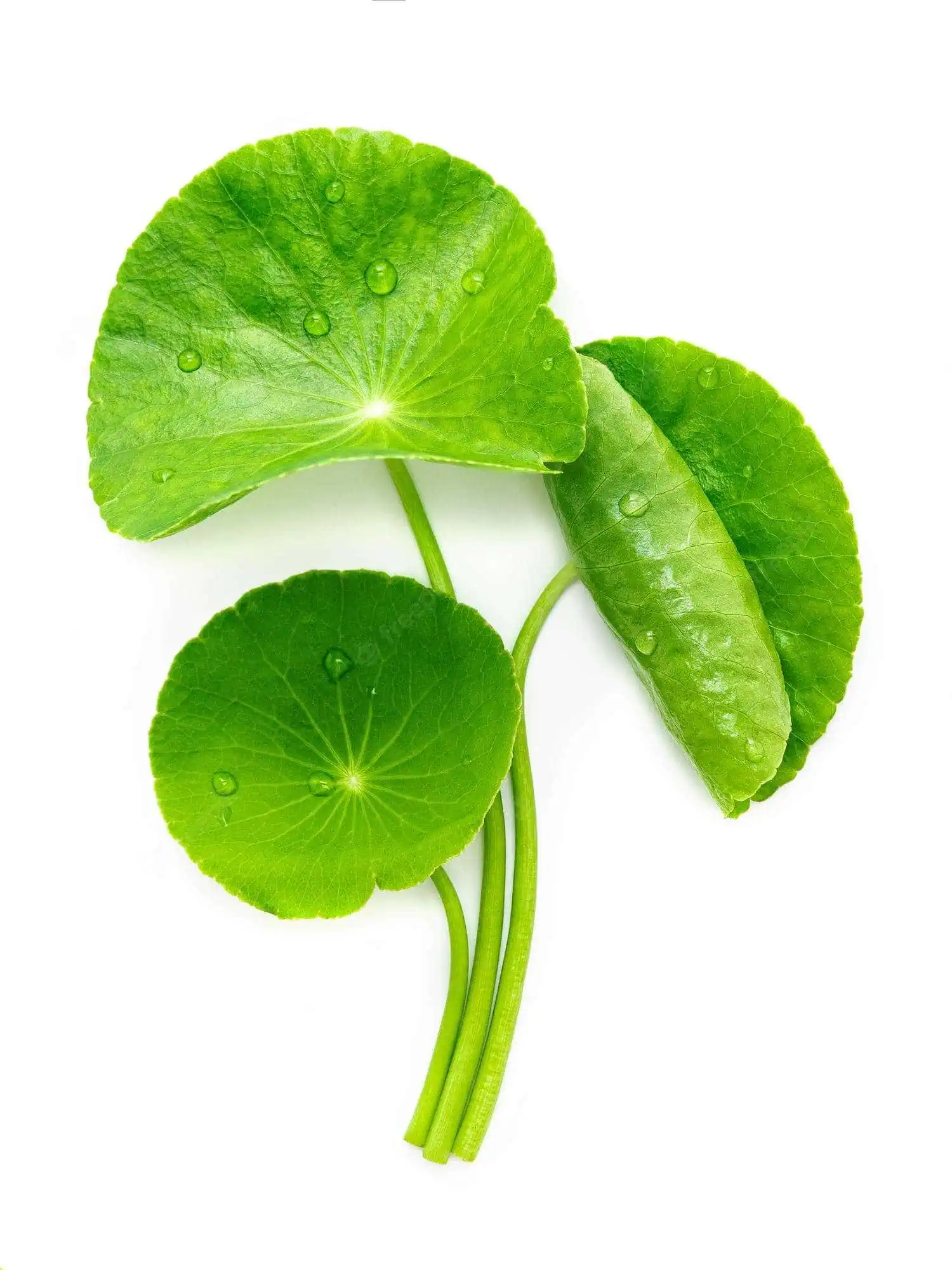
✦ Plant exosomes
A wide variety of plants and their fruits can be used as sources. For example, studies have shown the effectiveness of exosomes extracted from aloe, apples, turmeric, ginger, lemon, potatoes, radishes, pears, broccoli, grapefruit, grapes and strawberries.
More modern and high-tech cosmetics, such as MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes, use exosomes derived from the totipotent callus cells of certain plants – Panax Ginseng and Centella Asiatica.

Callus cells are a plant analog of human stem cells with the highest possible regenerative potential.
An important advantage of plant sources is the relatively low cost of exosome extraction and purification. This reduces the price of MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes while maintaining its high efficacy.

✦ Human exosomes
It may seem that using human exosomes is the most effective strategy. However, there are some serious problems:
- Obtaining exosomes from human cell cultures is an extremely complex and very expensive procedure, which affects the price of the final product.
- The problem of immunological incompatibility. By themselves, even human exosomes have extremely low immunogenicity. But at the same time, they contain proteins and genetic material from another person. According to some researchers, this can cause problems for the recipient similar to those that occur with organ transplants.
- Ethical issues. Human exosomes are isolated from stem cell cultures, which may be derived from sources such as the placenta detached after childbirth. Such sources may not be acceptable to everyone.
Conclusion
Exosomes are a safe and effective tool for skin renewal by activating signaling pathways, enhancing intercellular communication and naturally stimulating intracellular metabolism. Exosomes have universal action, high biocompatibility, low immunogenicity and almost no side effects. MEAMO Jeunetique Exo will give you all the benefits of bacterial and plant exosomes while eliminating the potential risks associated with human exosomes.
The most important biological effects of MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes:
- Powerful reparative and regenerative action on damaged skin.
- Protecting the skin from damage caused by ultraviolet light and oxidants.
- Moisturizing the skin by stimulating the natural mechanisms of hyaluronic acid accumulation.
- Activation of the production of new collagen framework of the skin by dermal fibroblasts.
The most important cosmetological effects of MEAMO Labs Jeunetique Exo Exosomes:
- Restoring the appearance of the skin, increasing its smoothness and elasticity.
- Elimination of fine and medium wrinkles.
- Lifting of soft tissues that have fallen as a result of the natural aging of the skin.
- Elimination of the consequences of acne – small scars and residual inflammation.
- limination of pigmentation caused by aging.
Many doctors and researchers prefer to classify exosomal products in the cosmeceutical category. This is the name given to preparations that are a combination of medicinal and cosmetic products. That is, they both treat your skin and take care of its appearance.